L2 Planet Issue #26
In this Issue of L2 Planet, we focused on the developments regarding DA, Linea, Celo, Arbitrum, zkSync, zkMIPS, Optimism and Starknet Ecosystem.
Data Availability Landscape
Did you hear of Data Availability before? It became a hot topic after Rollup Era rises and different Rollup designs occurs. So, what is Data Availability, and why it is important?
Data Availability means when you make a transactions on Blockchain, blocks contains transactions data and it can be downloadable and available for everyone who run a blockchain full node. In the context of Rollups, Data Availability has a critical role. Because Rollups execute transactions off-chain and send the relevant data as CALL DATA to the base chain or data availability layers. Thus, it allows users to execute transactions and validate the rollup chain. It also increases censorship resistance because the posted data can be used by prospective block producers to reconstruct the chain’s state and start producing new blocks. There are two types of Data Availability solutions exists:
On-chain Data Availability Storage: As most Rollups do, storing data on a blockchain. This blockchain can be any blockchain. Rollups will inherit the blockchain’s security and trust assumptions in terms of data availability.
Off-chain Data Availability Storage: Like Validiums do, storing data on an external solution. This external solution can be a centralized service controlled by an assigned committee or can be a decentralized data storage network.
Storing data off-chain a far way cheaper than storing on-chain. Projects may intend to use off-chain data storage to reduce transaction costs but this will change the security assumptions of Rollup. As you see image below, there are three methods when we store data off-chain.
Here is the list of projects which use off-chain data availability:
Immutable X - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Metis Andromeda - Optimistic Chain, Using MemoLabs for Data Availability
ApeX - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Sorare - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Rhino.fi - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Arbitrum Nova - Optimistic Chain, External Data Availability with a committee
Myria - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Canvas Connect - Validium, External Data Availability with a committee
Linea
Consensys’s type-2 zkEVM solution, Linea, is live on mainnet!
Linea is fully EVM compatible, which means existing smart contracts on Ethereum can be seamlessly deployed on Linea without needing to re-write or audit them. Linea also gets benefits backed by Consensys. So, development frameworks like Truffle and Metamask are supported.
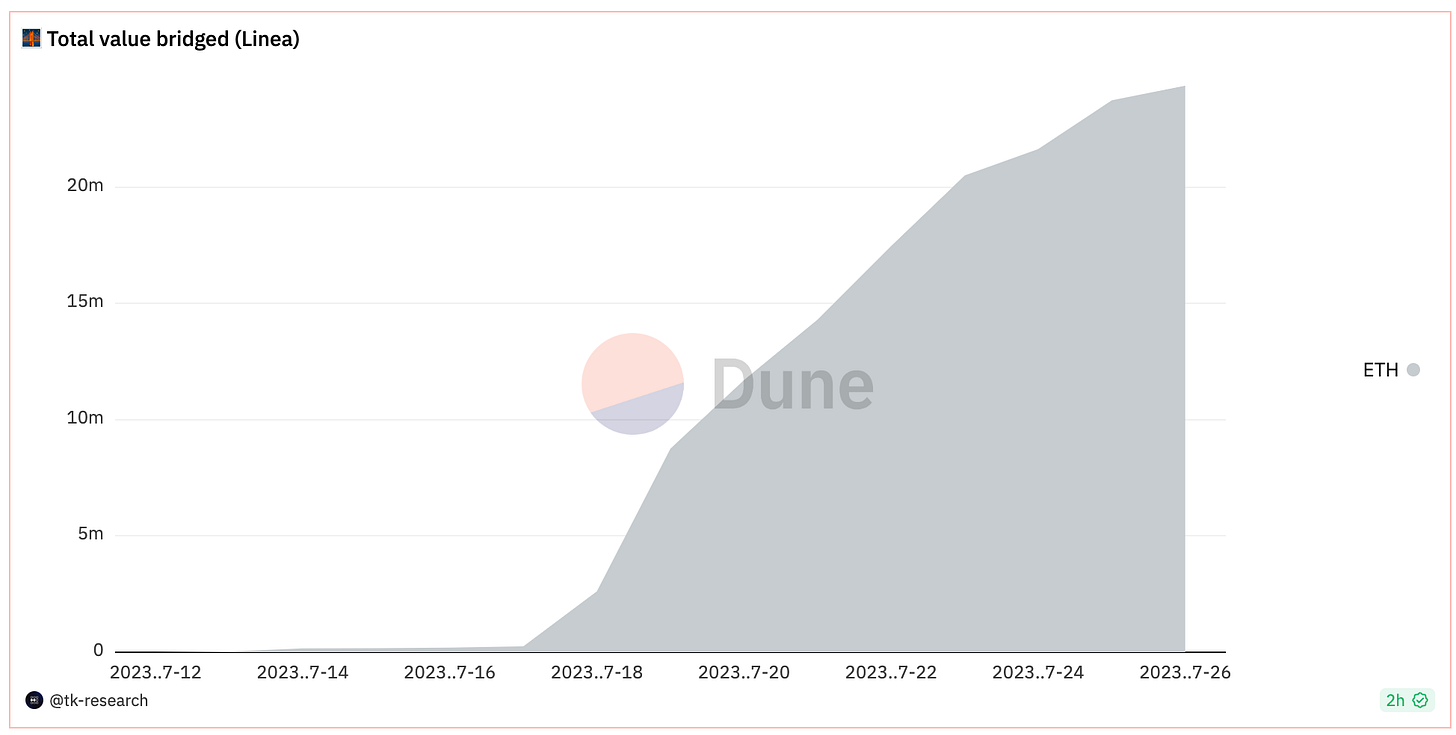
While only one week passed after the mainnet launch, Linea surpassed the $20m total value locked.
More than 450k wallet addresses were created and nearly 1m transactions have been done. Airdrop hunters working hard, huh?
Celo L2
All the Layer-1s will be Ethereum Layer-2 one day. Ethereum maxi frequently says that. Will it be real one day? Celo, a mobile-first, carbon-negative PoS blockchain decide to be Ethereum Layer-2!
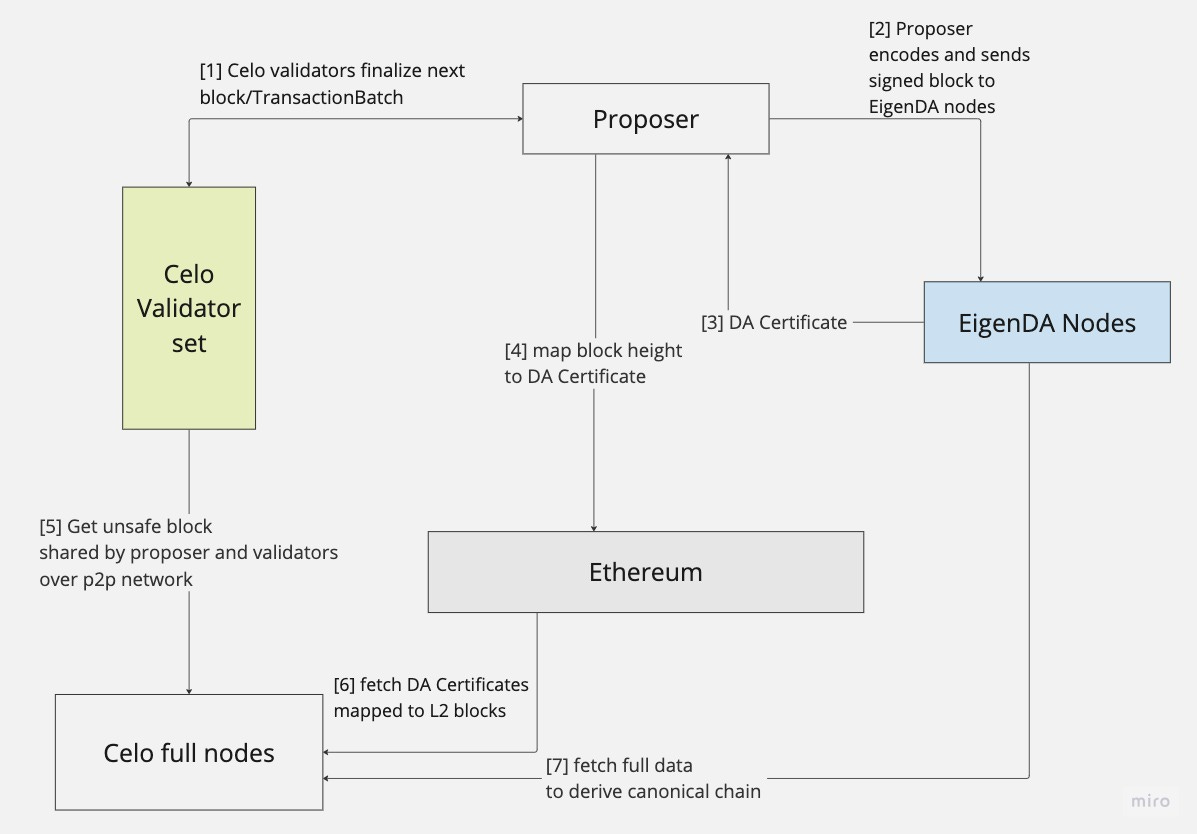
According to the announcement, Celo will leverage Optimism’s OP Stack. Celo’s existing validator set will be used to decentralize the sequencer and EigenLayer’s EigenDA will be used for Data Availability. In this design, Celo’s 1-block finality will retain. The proposed system looks as follows:
Welcome to the Layer-2 world Celo!
AIP-2
Arbitrum Improvement Proposal 2 (AIP-2), which is designed to enable the broad adoption of Account Abstraction on Arbitrum, has passed!
In this proposal, an adjustment was made to Arbitrum’s sequencer that will make more Account Abstraction significantly easier to implement. The necessary quorum has been passed on July 16.
When the implements have been done, Arbitrum gains a lot of fancy features such as social recovery, custom signature schemes, batched txs, session keys, etc. Arbitrum deserves that!
zkSync Boojum
zkSync planning to transition from SNARK based to STARK based proof system. Say hello to Boojum!
Boojum is the name of zkSync’s Rust-based cryptographic library. It is an implementation of RedShift (FRI + Plonk) and borrowed some dope ideas from plonky2.
The reason for this transition is simple: scalability. The team thinks that the current SNARK-based proof system won’t handle the volume of hyperchains. The team also wants to decentralize the proof generation. Boojum Prover runs on consumer-grade GPUs requiring only 16 GB GPU RAM. The Boojum repo is also open-sourced and waiting for contributions.
Boojum is now live on Mainnet, generating and verifying ‘shadow proofs’ today with real production data so that the team can carefully test the system ahead of fully migrating.
zkMIPS
ZKM team proposed a project called zkMIPS, a zero-knowledge VM based on MIPS architecture.
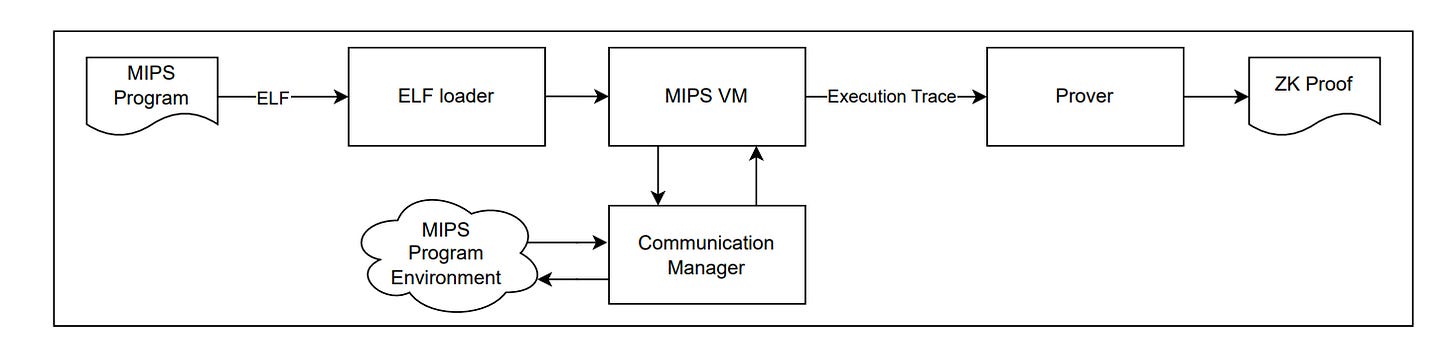
Any program written in C, Go, Rust, etc., can be compiled using a generally available MIPS compiler into MIPS R3000 BE ELF executable. The resulting ELF file is loaded into MIPS VM with the ELF loader. The VM executes the input executable. The communication Manager implements syscalls handlers, which can be used by the MIPS program during execution. Finally, the MIPS VM generates an execution trace for the Prover. The Prover then creates a ZK Proof.
According to the design, zkMIPS potentially leads to a reduction in the withdrawal period from the current 7-day duration to shorter timeframes for Optimistic Rollups. So, another term rises, Hybrid Rollups! Metis Andromeda Optimistic Chain planning to use and implement zkMIPS design and facilitate withdrawals. An example of a Hybrid Rollup looks like the image below.
Optimism Stack ZKP
RICS Zero and O(1) Labs won the contest of enabling ZKP for OP Chains.
In O(1) Labs solution they proposed the integration of a fault-proof-program-compatible MIPS VM (Virtual Machine) with advanced capabilities. This MIPS VM will work seamlessly with a Nova-folding-style bn128-kzg-plonkish system.
The proof system uses Kimchi, Mina’s state-of-the-art PLONKish system. The proposal wants to change the current Pasta-IPA backend with a bn128-KZG commitment scheme. So, the change allows for practical verification on the Ethereum L1 blockchain without non-standard precompiles, providing more flexibility and efficiency. Also, To streamline the communication between the blockchain and the MIPS VM, the proposal suggests optimizing the OP stack system with deep Keccak support. This improvement reduces the number of hashes and speeds up information retrieval.
Looks like OP Stack will enable the ZK Proofs soon :)
Starknet Appchains
Starknet has introduced Starknet Appchains, a modular framework that allows developers to create application-specific blockchains within its ecosystem using the Starknet Stack tooling kit.
Currently, Starknet Stack has different components with various options to use. Some of these options are in development but we have at least one option free to use. Here is the full list of component options.
Also, the first Starknet appchain was announced. Paradex, a perpetual trading exchange, became the first Starknet appchain.
Spectating Corner
Reading Corner
Research: Data & Function Privacy Architectures, zkValidator
Emerging ZK Use Cases, zkValidator
zkMesh: June 2023 recap, zkMesh
Upgradeability of Ethereum L2s, L2Beat
That’s all from L2 Planet for now, hope to see you in 15 days :)